new posts in all blogs
Viewing: Blog Posts Tagged with: Pub year: 2014, Most Recent at Top [Help]
Results 1 - 7 of 7
How to use this Page
You are viewing the most recent posts tagged with the words: Pub year: 2014 in the JacketFlap blog reader. What is a tag? Think of a tag as a keyword or category label. Tags can both help you find posts on JacketFlap.com as well as provide an easy way for you to "remember" and classify posts for later recall. Try adding a tag yourself by clicking "Add a tag" below a post's header. Scroll down through the list of Recent Posts in the left column and click on a post title that sounds interesting. You can view all posts from a specific blog by clicking the Blog name in the right column, or you can click a 'More Posts from this Blog' link in any individual post.
A few days ago, I began to see Sujei Lugo's tweets about Kenneth Oppel's The Boundless. Intrigued, I got a copy from the library. Published in 2014 by Simon and Schuster, here's the synopsis:
The Boundless, the greatest train ever built, is on its maiden voyage across the country, and first-class passenger Will Everett is about to embark on the adventure of his life!
When Will ends up in possession of the key to a train car containing priceless treasures, he becomes the target of sinister figures from his past.
In order to survive, Will must join a traveling circus, enlisting the aid of Mr. Dorian, the ringmaster and leader of the troupe, and Maren, a girl his age who is an expert escape artist. With villains fast on their heels, can Will and Maren reach Will’s father and save The Boundless before someone winds up dead?
The country that train is crossing is Canada. In chapter one, Will ends up driving the final stake--a gold one--into the tracks, thereby completing the track in Craigellachie, presumably in 1885.
Let's step out of the book and look at a little bit of history.
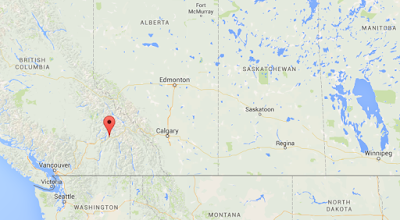
The final stake connecting the eastern and western portions of the Canadian Pacific Railway was driven into a railroad tie on November 7, 1885, in Craigellachie. Here's a map showing where it is, in British Columbia:
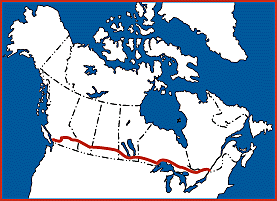
And here's a map from the
website of the Canadian Museum of History, showing the route of the Canadian Pacific Railway:
Prior to the arrival of Europeans,
all that land belonged to Native Nations.
In the US, the last spike of the Transcontinental Railroad was driven into the track in 1869. Train stories about railroads are popular. I read them with a critical eye, wondering if the author is going to provide readers with any information about what the railroads meant for Native people. They were, in short, a key reason land was taken from Native Nations. It is with that knowledge that I read books about railroads and trains.
The Boundless came out in 2014--the same year that Brian Floca's
Locomotive won the Caldecott Medal.
The synopsis (above) for
The Boundless doesn't mention anything about Native people, but the story Oppel gives us has a lot of Native content. Let's start with Mr. Dorian. We first meet him at the end of chapter one, when he captures a sasquatch. The year for that chapter is 1885. Chapter two picks up three years later (1888).
The next time we see Mr. Dorian is in chapter three, where, in his role as circus master, he talks to passengers about the train, saying:
Cut from the wilderness, these tracks take us from sea to sea, through landscapes scarcely seen by civilized men.
I was intrigued about Oppel's treatment of sasquatch in chapter one. The sasquatch Mr. Dorian captured becomes part of the circus (though it doesn't do anything in performances) and is on the train three years later. I wasn't keen on seeing that one captured and put in a cage because the sasquatch is in Native stories of tribes in the northwest. And, I didn't like reading "scarcely seen by civilized men" either because it suggests that the peoples of the northwest tribal nations were uncivilized. Reading that line, of course, reminded me of the grueling discussions about "civilized" Indians in
The Hired Girl (those discussions took place on Heavy Medal and prompted me to do a stand-alone post,
A Native Perspective on The Hired Girl).
Those two concerns jumped to a whole new level when I got to chapter seven and learned that Mr. Dorian is Native. The bad guy, Mr. Brogan, is looking for Will (the protagonist). Brogan thinks Dorian is hiding him and threatens to throw Dorian and the entire circus off the train. Dorian doesn't think Brogan has the authority to do that, and Brogan says (p. 124):
"You'd be surprised. And I don't take my orders from circus folk--especially half-breeds like you."
We're not supposed to like Brogan, so having him use "half breed" is supposed to provide us with a cue that the use of the phrase is not ok. Even so, I cringed when I read it. Such words--even when uttered by despicable characters--sting.
That said, it was hard for me to think of a Native person capturing a sasquatch and keeping it in a cage (he also wants to catch a Wendigo, which is also a problem), and it is hard for me to think that a Native person would say that Native homelands were "scarcely seen by civilized men." Would he think that? Maybe it is a script he uses as a circus ringmaster? A performance designed to stir up the imagination of the (white) audience? If so, Oppel should have given readers a clue about those words, but he didn't.
Either way, portraying Native peoples and our nations as "primitive" or "uncivilized" fits with white supremacy and ideas that we didn't know how to use the land (as Europeans used land), and therefore the land itself could simply be claimed by European nations and Europeans who knew what to do with it (by their definition, of course).
Back to the story...
Mr. Dorian doesn't like being called a "half breed" and calmly replies that he prefers the term Métis. Will overhears their conversation and thinks:
Having grown up in Winnipeg, Will is familiar with the Métis--the offspring of French settlers and Cree Indians--and the insults they endured, especially after their failed uprising.
Is what Will says accurate? Partially, but there's a lot more to it than that. And, is the "failed uprising" about Louis Riel? And... why use "uprising" to refer to that period of Métis activism? What image of comes to mind with the word "uprising"? Is it one like this? This is Riel and men who were, in the late 1860s/early 1870s, part of a provisional government he formed:
 |
| Source: http://www.mhs.mb.ca/docs/events/rielcouncillors.shtml |
Other words in what Will says about Métis are odd, too. Uprising is one, but so is "offspring." Technically, it does mean children, but why not have Will use children, or kids?
Skipping ahead now, to page 145 (chapter 8) where Maren (she's a main character, too) is showing Will around the train car where the circus performers practice. Specifically, they're looking at the trapeze artists (the train is huge):
Both men are lean and muscular. Their heads are bald except for a tuft of long hair at the back, which is gathered into three braids.
Will asks Maren if they're Mohawk. She says yes, and that they're fearless, that heights mean nothing to them. I don't know about those three braids, but Oppel is definitely using what he knows about
Mohawk steelworkers. Fearless, though? Nope.
In chapter nine, Will is headed up to the "colonist" cars which are overcrowded. The person who takes them through the cars tells them that (p. 177):
"These people are fortunate to get passage on the Boundless at all," Drurie says with a sniff. "They're the poorest of the poor, and they've washed up on the shores of our country to claim our land."
They're German, French, and Italian. Mr. Dorian replies to Drurie (he's white):
"My mother's people are Cree Indian. Perhaps it's people like you who have washed up on our shores. A stimulating thought, don't you think?"
Drurie ignores him, but let's pause. Remember what I pointed out about Dorian's use of "civilized" in chapter three? Dorian is expressing a very political point here, but didn't do so earlier. That is an inconsistency in his characterization. Of course, I like the point he makes here. That line gets at current political discussions about immigration.
There's more I could note (like the
brownface Sujei Lugo pointed out), but I'll end with a brief discussion of the buffalo hunting scene. It takes place in chapter 12. The train has a shooting car, in which passengers can pay to use a rifle (provided by a steward) to shoot at wildlife they pass. Just at the moment that Will and Maren are in the shooting car, a herd of buffalo moves over a hill and toward the train. Passengers start shooting at them. Will thinks it unsportsmanlike. He's right, of course, but that activity was common on trains during that time. Mr. Dorian says (p. 251):
"This is how you exterminate a people," the ringmaster says bitterly, "You kill all their food."
Then, passengers see Indians riding behind the herd, driving the herd away from the train. Some have rifles and some have bows. The steward tries to get people to leave the car, but they don't want to. One man shouts (p. 252):
"Damn redskins! They're steering them away from us."
Angry, that man then takes aim at one of the Indians on horseback. Dorian grabs the rifle and tells the angry man that the Indians need those buffalo for food and hides. The angry man says he's helping them by shooting the buffalo. Dorian points out that the man was shooting at the Indians, and the man says:
"What's one less Indian?"
He's killed an instant later, by an arrow, and Dorian murmurs "one less white man." The steward manages to get everyone inside, where Will hears a man call out how they "showed those redskins."
Earlier, I talked about a bad-guy using "half-breed." Here, the people using "redskins" are not likable either, and that's supposed to help readers know that what those men are doing is not ok. I think it does that, but as before, such language stings. In this case, it is even worse.
I don't like
The Boundless. Like many of Oppel's books, it has sold well. It got starred reviews from the major children's literature journals--stars, in my view, it does not merit. Given its inconsistencies and use of troubling ideas and phrases, I cannot recommend Oppel's
The Boundless.
I read Alaya Dawn Johnson's Love is the Drug in 2014 when it came out. I think Ebony Elizabeth Thomas, or maybe Edith Campbell, told me about it. Elsewhere, I've written about books with a problematic line about Native people or culture, or, what we could call a microaggression.
Johnson's book is not about Native people or culture, but she does have a few lines in it that I want to call attention to--because they are the opposite of a microaggression. Indeed, I find them affirming.
They're about the Washington DC professional football team. You know the one I mean: the Redskins. On page 44, Emily and her dad are talking about the team's losing streak. He tells her it is because of their name, that it gives them bad luck. She's a bit skeptical. She thinks it is more about the players and their abilities. I enjoy their banter. He also makes the point that the team name is offensive, when he asks her if the team could get away with calling themselves the Washington Niggers. Pretty bold, but also quite effective.
Later, there's a part where one of the bad-guy-characters is talking about Thanksgiving--and the football game scheduled for that day. He says (p. 215):
"I hear the Redskins are going to play Dallas in a demonstration game. The good American spirit, cowboys versus Indians. The Indians will lose, of course. Everything is going back to normal."
I won't spoil the book for you by elaborating on what "normal" is... Here's the synopsis:
From the author of THE SUMMER PRINCE, a novel that's John Grisham's THE PELICAN BRIEF meets Michael Crichton's THE ANDROMEDA STRAIN set at an elite Washington D.C. prep school. Emily Bird was raised not to ask questions. She has perfect hair, the perfect boyfriend, and a perfect Ivy-League future. But a chance meeting with Roosevelt David, a homeland security agent, at a party for Washington DC's elite leads to Bird waking up in a hospital, days later, with no memory of the end of the night. Meanwhile, the world has fallen apart: A deadly flu virus is sweeping the nation, forcing quarantines, curfews, even martial law. And Roosevelt is certain that Bird knows something. Something about the virus--something about her parents' top secret scientific work--something she shouldn't know. The only one Bird can trust is Coffee, a quiet, outsider genius who deals drugs to their classmates and is a firm believer in conspiracy theories. And he believes in Bird. But as Bird and Coffee dig deeper into what really happened that night, Bird finds that she might know more than she remembers. And what she knows could unleash the biggest government scandal in US history.
I enjoyed the story. Published by Scholastic.
This is my second post about Martina Boone's book. In April of 2015, I learned about Martina Boone's Compulsion: Heirs of Watson Island. Published by Simon Pulse (which is part of Simon and Schuster) in 2014, the protagonist is a teenage girl named Barrie who moves to a plantation in South Carolina to live with her aunt Pru. The story is set in the present day, but the past is very much a part of Compulsion.
The island where the plantation is located is haunted and the house is falling apart. Having read it, I do not recommend Compulsion.
Notes as I read:
On page 61, Barrie is at the river. She sees a ball of fire hovering over the water. It gets dimmer and the river itself seems to be burning. The flames travel to a "shadowed figure of a man." Cupped in his hands is an ember (that is all that remains of that fire ball):
A cloak of black feathers covered his back and shoulders, and a matching feathered headdress melded into his long, dark hair.
He turned suddenly and looked at Barrie--straight into her--with eyes that were only lighter spots in a face painted with a war mask of black and red.
She blinks and he's gone, but "her heart was a drumbeat in her throat, war drums pounding, pounding a retreat" (p. 62).
Page 145: Barrie is with her cousin, Cassie, who tells her the history of the island. When the Carolina colony was being settled, the governor was gambling with Thomas Watson, a pirate. There are two other pirates gambling that night: John Colesworth and Robert Beaufort. Descendants of all three figure in
Compulsion. Watson accused the governor of cheating. Later when it came time to give out land grants, the governor took revenge on Watson by giving him land on a haunted island. Barrie asks, "Haunted?" and Cassie replies:
"Yes, haunted. Thomas Watson's island was inhabited by the Fire Carrier, the ghost of a Cherokee witch who had cleared his tribal lands of malicious spirits, yunwi, and pushed them down the Santisto until they'd come to the last bit of land surrounded by water on every side. The Fire Carrier bound the yunwi there, and kept them from escaping, with fire and magic and running water."
Early on, Watson had tried many times to build a mansion on that land but overnight, whatever he'd built during the day disappeared. Another pirate, Colesworth, offered (p. 145):
"to get one of his slaves to trap the Fire Carrier and force it to make the yunwi behave."
The slave was a voodoo priest, Cassie tells Barrie (145-146):
"He trapped the Fire Carrier at midnight when the spirit came to the river to perform his magic, and he held the Fire Carrier until the witch agreed to control the yunwi and make them leave Thomas Watson alone."
Then, they made the
yunwi give Watson back everything they'd taken from him. And then they trapped the Fire Carrier again and demanded that he help Beaufort win a woman's heart. That woman was already in love with Colesworth, but thanks to the Fire Carrier, Beaufort seemed to know whatever the woman wanted. Eventually, he won her over and they were to be married, but Colesworth had the voodoo priest capture the Fire Carrier one more time, hoping to get the woman back. But the Fire Carrier was tired of being used. He overwhelmed the voodoo priest and put a curse and gifts on the three men. Future Colesworth generations would be poorer and unhappier than the Watsons. That's the curse. The gifts? The Watson's would always find what they'd lost, and the Beauforts would always know how to give others what they wanted.
Barrie is a Watson. Cassie is a Colesworth. Because of the curse, she's poor and wants Barrie to use her gift of finding things to help her find the Colesworth valuables, buried by an ancestor before the Yankees burned Colesworth Place down. Barrie isn't sure she wants to help her.
That night, Barrie heads out at midnight and sees the Fire Carrier again. She sees him better this time (p. 159):
The glistening war paint on his naked chest, the feathers in his clock and headdress stirring in the breeze...
He wears that red and black mask again. He stares at her again and then walks away. This time, she sees shadows, too, and realizes they are the
yunwi. And, she smells sage burning. She thinks he wants something from her.
Later when she is talking with Pru, Barrie learns that her aunt feeds the
yunwi at night and that they take care of the garden. When they're outside, Barrie feels a tug from the woods. Pru tells her not to go there.
On page 273 she goes outside again at midnight. This time she's in socks. As she runs about, she gets cuts from gravel and shells on the path. She slips and cuts her palm, too. She washes the blood of her her palms in a water fountain. It seems her blood runs in ribbons through the water, and that she can see human figures in the shadows. She sees the Fire Carrier again. He points to something behind her. She looks at the top of the fountain and sees a spirit. It is a woman whose torso and legs are a column of water. Barrie asks her what she wants, and she says "You have given blood." and then "We accept the binding." As she walks back to the house she realizes the
yunwi are swarming around her bloody footprints. She pulls off her socks and throws them to the
yunwi, telling them to "eat up." It occurs to her that she can use those bloody socks to barter. She grabs them back up and tells the
yunwi that they'll have to give back things they took from her. Turning back to the house she finds her missing things and missing screws, too, that they'd taken when making mischief in the house. She throws the socks back down to the
yunwi and tells them not to break anything else, or take anything else, either, from her or anyone else. Through her blood, Barrie has power over the
yunwi.
From there, the
yunwi are around her a lot but don't figure much in the story. They more or less accompany her around.
Fast forward to page 375 when Barrie's gift draws her out to the woods. With Eight, the two walk towards a particular tree that is pulling at her:
"I've heard of this tree." Eight followed her toward it. "The natives around here used to call it the Scalping Tree and hang the scalps of their enemies on it."
The tatters of Spanish moss did look eerily like scalps. Barrie shivered despite the still-warm air. "Why?"
"I don't know. I don't even know which tribe it could have been. None of them, probably. The Fire Carrier was Cherokee, but since he brought the yunwi here from somewhere else, he clearly wasn't local."
Barrie finds the spot that is pulling at her, digs, and they find a metal box that has keys that gives them access to a room, and a staircase to a tunnel. There's a pull from there, too. Barrie and Eight (and the
yunwi) go down the stairs, unlock another door and find that lost treasure Cassie wanted her to find. That's not the source of the pull, though, so they go a bit further. The
yunwi find the source first: two skeletons. Barrie and Eight hear something behind them and see that Cassie has followed them. She grabs the bag of treasure and takes off, locking them in that tunnel. Barrie asks the
yunwi to get them out but they don't go near the door. Why? Because the door is made of iron, and iron hurts them.
Barrie and Eight decide to head on through the tunnel. The
yunwi go with them. Eight says it may have been an escape route "during the Yamassee uprising" or "other Indian raids before that." When they come to a fork, they choose one and follow it. Barrie realizes the
yunwi have stopped at the fork. They watch, forlornly. "[S]he was leaving them locked up here alone in the dark" (p. 398). She tells them she'll come back and let them out. That tunnel is to an iron door they can't get through. They try the other one and eventually find one that doesn't have the magical protection (things don't rot) that the others do. She gets out but runs into Ernesto (he's got tattoos all over, speaks Spanish) and Wyatt (Cassie's dad) who, it turns out are drug runners.
While tussling with them, the hour turns to midnight. She smells sage, and the Fire Carrier sees her struggling. He sends fire that causes Ernesto and Wyatt's boat of drugs to explode. She gets away, climbs out of the water and sees the Fire Carrier, up close (p. 422):
In the rushes before her, the Fire Carrier stood close enough that the war paint on his face and chest shone slick with grease. Veins stood out on his arms, and every lean muscle of his chest and stomach seemed defined and ready to spring into action. But apart from the feathers on his clock and headdress stirring in the night air, he was motionless. He watched her.
She sees that he's about her age. His eyes are sad. She wonders why he's been doing this midnight ritual of lighting the river on fire year after year. She understands he wants something from her. He heads off to the bank and she realizes she can almost see through him. Hearing splashing she's afraid it is Ernesto or Wyatt, but it is Eight. In the next (final) chapter, Wyatt is dead. Cassie and Ernesto are missing. The bodies from the tunnel are brought out (they're Luke and Twila. Luke was Barrie's great uncle and Twila was Eight's great aunt. They're part of a rather layered mystery element of the
Compulsion.)
Barrie thinks about how the Fire Carrier saved her life. No mention of the
yunwi.
The end. Of this book, that is.
Compulsion is the first of a trilogy.
My thoughts on the Native content of Compulsion
When we first meet the "Fire Carrier" of this story, Boone gives us things commonly (and stereotypically) associated with Indians: feathers, painted face, drums. This land was haunted before Barrie's ancestor was given this land. I may have missed it, but I don't recall reading why that land was haunted.
We know the Fire Carrier is there now, and that he's ghost-like (remember Barrie can see through him), so he's definitely haunting that land now. He, we read, is a Cherokee witch. If you look up the yunwi, you'll likely find references to Cherokee Little People. If you go to the Cherokee Nation's website, you'll find
information about them. Some of what Boone tells us about the yunwi aligns with information at the website, but Boone's yunwi are cannibals. Remember? They swarmed over her bloody footprints. That doesn't fit with what I read on the Cherokee Nation site, but it does fit with some false but common ideas of Native peoples as being cannibals. It is odd, too, that Boone's yunwi can't go near iron. I don't see that on the Cherokee site, either. From what I understand, the Little People are independent, acting on their own, significant to Cherokee ways of being in, and understanding, the world. But Boone's yunwi can be controlled by... a white girl. Echoes of
Indian in the Cupboard, right?!
Then there's that scalping tree... Setting aside the outlandish idea of a "scalping tree" let's look at what Eight said about that tree. He assumes it can't be associated with the Cherokees because they weren't "local" to that area. Maybe... but maybe not. The
South Carolina website tells us Cherokees were in South Carolina at the time it was established as one of the 13 colonies.
In all honesty, I find the Native content of
Compulsion to be inaccurate and confusing. And troubling, too.
As I read, I came across some other troubling content. Cassie is in a play. The play?
Gone With the Wind. I came upon that part the day after the murders in the Emanuel AME Church in Charleston. It stopped me cold.
I wrote up my thoughts, then, right away. Nothing I read as I continued alleviated those concerns.
I'm also unsettled by Ernesto.
It seems to me that Boone has, unintentionally, wronged three distinct groups of people and readers in the US: American Indians, African Americans, and Latinos. What will she do in the next two books of this trilogy?
In an interview, she indicates her character will grow through the series, but I've given that idea some thought and find it wanting.
I'm closing this post with a quote from Anonymous, who submitted this comment to my previous post about
Compulsion:
I find the idea of a reader -- particularly a child -- having to wait to see herself humanized an inherently problematic one. Yes, it might accurately reflect the inner journey many white people take, but isn't the point that our dehumanizing views were always wrong? And therefore, why go back and re-live them? Such ruminations could definitely be appropriate in an all-white anti-racist group, in which the point is for white people to educate each other, but any child can pick up a book, and be hurt--or validated--by what's inside. Asking marginalized readers to "wait" to be validated is an example of white dominance as perpetuated by well-intentioned white folks.
Need I say that I do not recommend
Compulsion?
Back in April of 2015, I learned about Martina Boone's Compulsion: Heirs of Watson Island. Published in 2014 by Simon Pulse (which is part of Simon and Schuster), the protagonist is a teenage girl named Barrie who moves to a plantation in South Carolina to live with her aunt Pru. The setting is present day.
The island where the plantation is located is haunted, and the house is falling apart. Later, we'll read about malicious Cherokee spirits called "yunwi" who are doing things (loosening screws and the like) to the house at night so that the next day, things come apart when touched. Outside in the garden, however, they are helpful. If Pru leaves food out for them, they will tend the garden.
This is my first post about the book. I've not finished reading it yet. My decision to post right now, before I finish it, is deliberate.
The book is set in Charleston. I started reading it Wednesday afternoon. That night, nine African Americans were murdered in Charleston. When I woke up on Thursday, my social media feeds were about the murder of nine people who were killed in a historically black church of deep significance, by a white person who said [Y]ou've raped our women...
I read the news stories and then, returned to Compulsion. I came to a part that brought me up cold. On page 150, Cassie (one of the main characters), tells Barrie:
...my theater group and I do Gone With the Wind at night, in front of the ruins.
I read that line and paused. I imagine a lot of readers will pause, too, but that a lot more won't. Most will just keep on reading. Far too many people don't see the novel or movie as racist. (The "ruins" are what is left of Cassie's family plantation.)
After I ruminated on that for a while, I read on. I wondered if Boone (the author) would, in some way (through a character or through the narration), critique Cassie or her group for doing that play.
I didn't find anything more about it until I got to page 237. Barrie and Eight (her love interest) are at the play. The play opens with Cassie and two boys coming onto the stage. They're wearing "aristocratic costumes" and are followed by
...a girl dressed as a slave, who balanced glasses and a pitcher of lemonade on a tray.
Barrie and Eight are engrossed by the production (p. 238):
Neither of them moved again until the audience gasped when Rhett Butler came on stage, played by a light-skinned African-American boy.
"Oh, that's brilliant," Barrie whispered. Everyone around her whispered too, but then the magic of the play took hold again.
When the play is over, Eight wonders "if that was nerve or genius." Barrie replies that it is both. End of discussion. I assume they're talking about casting an African American as Rhett. And, I assume that the girl playing "the slave girl" is white.
I have a lot of questions at this point.
Why were they doing that play in the first place? Since the author includes it without comment, is she among the millions who don't see it as problematic? Or, who have nostalgic attachments to it, such that they can't set it aside?
Why "a light-skinned" boy? Why not just say "African American boy"? Was it necessary that he be light skinned? What does it mean to have an African American boy in this racist play? It reminds me of Ann Rinaldi's
My Heart Is On the Ground, in which a Native girl happily plays a Pilgrim in a Thanksgiving play.
I assume that we (readers) are supposed to think that Cassie is enlightened for casting a light skinned African American as Rhett. We're supposed to think that there is racial progress in Boone's Charleston. I don't see racial progress at all, but I wonder if Boone imagined me, or any person who casts a critical eye on
Gone With the Wind as a reader of her book? As presented, it reminds me of
The Help where good white people help black people.
In interviews of her, I've read that Boone's characters are going to change over the three books. Maybe Boone is going to have Barrie and Cassie step away from
Gone With the Wind. Maybe they're going to say "it was dumb for us to do that" or something like that. That is what characters do, right? They change over the course of a story.
I want to poke at that idea a bit.
Let's assume that by the end of the trilogy, Barrie or Cassie (or both of them) reject
Gone With the Wind. Readers will move with them to that point. It'll be a win for social justice. But who is it a win for?
Some readers will applaud when Barrie or Cassie see the light. But what about black teens who already see that light? They are asked to be patient until Barrie and Cassie see that light. They, who are the target of racist acts today, have to be patient.
I find it deeply disturbing. The instant that the play is mentioned, somebody in the book has to say WTF so that
immediately, readers will think differently.
Am I making sense? Do you get what I'm saying? Help me say it better so that writers won't do what Boone has done.
There's so much more to say.
The white man who murdered nine African Americans in Charleston said "you rape our women." Did you know that there are heated discussions within some circles about whether or not
Rhett raped Scarlett? In Boone's book, Rhett is African American. My guess? Boone and her editor had no idea that some would read Rhett-as-African-American as a negative rather than the plus they intended it to be.
Once I hit upload on this post, I'll return to
Compulsion. I have a lot of notes about the Cherokee witch and the voodoo priest. As a Native reader,
I gather I'm supposed to be patient, too, as a white writer speaks to white readers about racism, in the past, and in the present, too.
In July of 2014, Holiday House released The Mayflower written by Mark Greenwood. Illustrated by his wife, Frane Lessac, some people think it is a contender for the Caldecott. I sure hope not, but America loves its birth narratives and many segments of America refuse to see it in a balanced or accurate light.
Greenwood and Lessac provide that same romantic story, as shown on these pages (source: https://wondersinthedark.wordpress.com/2014/11/27/caldecott-medal-contender-the-mayflower/). Here's Squanto:
And of course, that meal:
For further reading:
Will we ever get to the point in time where creators of children's books stop showing kids playing Indian at Thanksgiving?!
Here's the cover of Pinkalicious: Thanksgiving Helper. In the story, Pinkalicious invites her brother to "pretend it's the first Thanksgiving." She puts on a pink feather and will be Princess Pink Feather (cue moans, groans, and lots of eye rolling). I guess Kann and her publisher and all the people who buy and read/review the book do not know that playing Indian--or Indian princess--is stereotyping of the worst kind, because it seems harmless and innocent and, to quote some of the reviews "cute!". It isn't harmless or innocent or cute. It is stereotyping and ought not be happening in a book published in 2014.
Pinkalicious: Thanksgiving Helper is not recommended.

By:
Debbie Reese,
on 5/27/2014
Blog:
American Indians in Children's Literature
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
middle grade,
middle school,
stereotypes,
not recommended,
Macmillan,
Copper Magic,
grave robbing,
Julia Mary Gibson,
Pub year: 2014,
Add a tag
In Copper Magic, twelve-year-old Violet Blake is digging by a stream near her house in Michigan and finds a "talisman" -- a copper hand that she comes to call "the Hand." Violet feels that this hand has some kind of power. She thinks she can use it to make wishes come true. Course, her first wish (for a new dress) does come true (actually she gets TWO new dresses), so she's thinking about how she'll use it to get her mom and little brother back home. Her mother is half Odawa.
Well, it turns out there was more than just that copper hand in the spot where Violet was digging. There's also a skeleton there that is dug up (another kid finds it), reassembled, and displayed as a curiosity in a local hotel.
Cue some fake Hollywood Indian music...
Can't be messing around in them Indian burial grounds, right?! We've seen THAT enough times in movies and TV shows to know that messing with bones and artifacts means bad things are gonna happen. And of course, bad things happen to the people in Copper Magic. Lots of bad things. A wicked storm. Lake water behaving in odd ways. Death. Before all that happens, Mercy (Violet's new friend) talks about how there might be a curse on the grave... Violet and her mother (remember--her mom is half Odawa) have special powers, too. They can see things other people can't.
"Cut!"
Cut that fake Hollywood Indian music, that is, and an emphatic "Cut it out!" as my parents would say when I was doing something wrong.
Cut it out, Julia Mary Gibson!
Cut it out, Susan Cooper!
Cut it out, Rosanne Parry!
"Cut what?" you may wonder... Quit writing about Native spirituality! You mean well, but you don't know what you're doing. From a place of ignorance, you're adding to an already-too-tall pile of garbage that gets circulated as information about Native people.
A good many writers have a moment in their life that touched them in such a way that they feel they must write about Native people. Gibson's moment is described in her Afterword. When she was eleven years old, she and her family found some bones near their summer cottage in Michigan. "[A]n expert" said they were "most likely American Indian but not old enough to be archeologically significant" (p. 329), so her grandfather "pieced together a skeleton and mounted it on plywood." Her "superstitious" grandma didn't like it and insisted the bones be reburied. This took place in the late 1960s or early 1970s (my guess, based on
Gibson's bio at Macmillan that says she was born "in the time of Freedom Rides and the Vietnam War").
Gibson goes on to say that her grandfather didn't know better.
In
Copper Magic, Violet is Gibson. The person who puts the skeleton on display is Mr. Dell, a hotel owner intent on increasing his business. The superstitious person who wants the bones reburied? Well, that is Mrs. Agosa, an Odawa woman who tells Violet to "Watch out for ghosts out by you" because "mad ghosts can throw out curses" (p. 134).
Gibson,
Cooper,
Parry and many other writers poke around a bit and pack their stories with bits of info that make it sound like they know a lot about American Indians. Gibson does that in
Copper Magic when she has some of her characters talk about grave robbing and why it is wrong. She also does that when she has Mrs. Agosa talk about the hotel owner burning her people's village and orchards because he wanted their land. In the Afterword, Gibson tells us that part of the story is true (p. 330):
"The real people of the Chaboiganing Band were yanked from their houses by a crooked land grabber and the local sheriff, who flung kerosene over homes and orchards and burned down the whole village, just as Mrs. Agosa tells it."
The burning of that village is important information. It is what major publishers like Macmillan (publisher of
Copper Magic) ought to make known. I wish Gibson had made it the heart of her story. Instead, she chose to tell a story about grave robbing, curses, and mystical Indians. There's more to the "mystical Indians" theme... Interspersed throughout
Copper Magic are pages about two ancient women: Crooked Woman and Greenstone. Those parts of Gibson's novel are presented in italics. They feed the mainstream monster of stereotypical expectations--where people love to read about "mystical Indians" and our tragic history.
In
Copper Magic, Violet's dad is a steady voice saying that Indian graves deserve respect and ought to be left alone. Violet parrots some of what he says but doesn't really understand. Ironically, Gibson is more like Violet than she realizes. Her understanding is superficial. Violet wants to use the hand to get what she wants. Gibson uses the childhood story to do what she wants.
As you may have guessed by now, I don't like what Gibson has done in
Copper Magic. And of course, I do not recommend it.
Copper Magic is another FAIL from a major publisher.