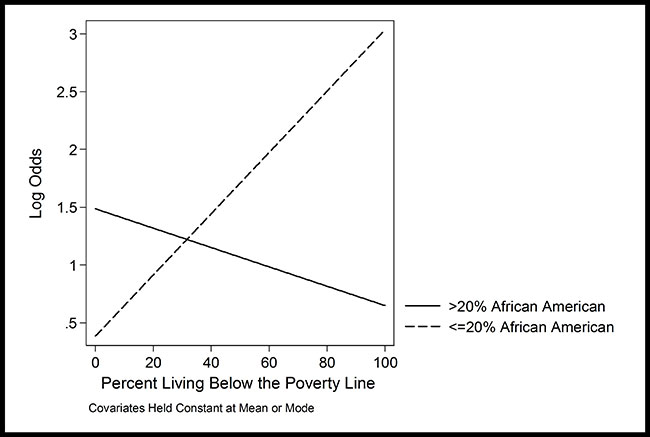
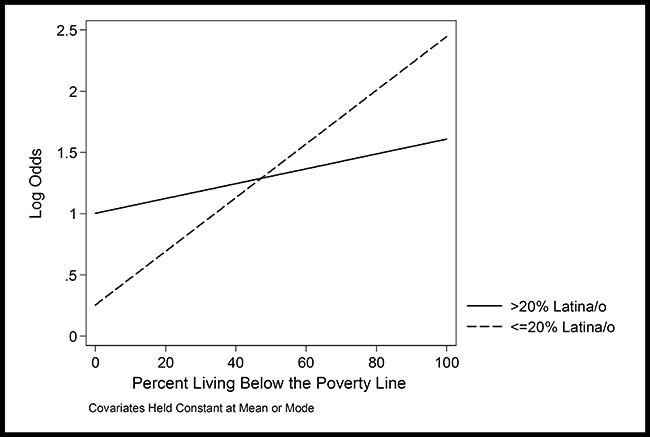
In our new How We Did It series, we shine a spotlight on the people and
In our new How We Did It series, we shine a spotlight on the people and
organizations doing important work to support diversity in publishing and beyond. Their stories and ideas are a dose of inspiration for all of us as we move forward in our work.
Today we are thrilled to have Kyle Zimmer, President, CEO, and Co-founder of First Book, with us. Here’s how Kyle describes her organization: “First Book supports educational equality by providing high quality, new and relevant books and educational resources to teachers and caregivers serving the millions of children growing up in low-income families.” Welome, Kyle!
How did First Book begin? Has the organization’s mission evolved since it was founded?
I co-founded First Book with two friends in 1992. I had been volunteering at a D.C. soup kitchen when I learned that not only were there no books available but the children didn’t have books at home either.
I started talking to other programs and schools and became aware of this enormous problem – with clearly disastrous implications – for individual children and our broader society. In a resource-rich country like ours, how can millions of children grow up without books, at home, at school and in their communities?
I became a student of the publishing sector and learned that the design of the industry makes it almost impossible to serve lower-income segments of the market. The publishing industry is based on  a consignment model – meaning that inventory that doesn’t sell at retail is returned to publishers. So, of course, retail book prices are set high, in part, to cover the cost of unsold inventory. Today in the U.S., the average cost of a premium children’s picture book is $18 – far beyond the reach of low-income families.
a consignment model – meaning that inventory that doesn’t sell at retail is returned to publishers. So, of course, retail book prices are set high, in part, to cover the cost of unsold inventory. Today in the U.S., the average cost of a premium children’s picture book is $18 – far beyond the reach of low-income families.
Our solution was to aggregate the voice and buying power of educators and programs serving children in need, and in the process, create a viable market that publishers can serve. The First Book Network has become the largest and fastest growing network of classrooms and programs serving children from low-income families. This enables us to purchase books and content that our Network needs in bulk and we can negotiate significant discounts as a result.
While our fundamental mission has not changed, our understanding of the issues of poverty and education has evolved. As a result, we’re expanding our offerings and our definition of what it means to enable educational equity. We are listening to the First Book Network and responding to their needs. Now we’re offering school supplies, refurbished laptops, nonperishable food items, and even winter coats and underwear – in addition to culturally relevant books and educational resources. If our educators request something, we’re going to go out and find the partners who can help provide it – with the best quality either for free or as close to free as we can get.
First Book has done amazing work to promote diverse books by essentially creating a new market for diverse titles. Can you talk a bit about how and why First Book decided to do this?
We developed the Stories for All project to address the needs expressed by the First Book Network. They are on the front lines and have seen that books focused on all-white characters and experiences just don’t connect with – and don’t represent – the children they serve. In a First Book survey, 90% of respondents indicated that children in their programs would be more enthusiastic readers if they had access to books with characters, stories and images that reflected their lives.
We heard this need loud and clear – so we began to build strategies that would elevate access to these resources. In an industry already facing fierce competitive pressures, it’s no surprise that publishers have chosen to stick with the content they know will sell. There is a high risk factor and high costs involved in developing new content and marketing to new audiences.
That’s why we launched the Stories for All project. And we decided to roll out the initiative in a big way: promising to purchase, on a non-returnable basis, half a million dollars’ worth of inventory from the publisher offering the best, highest quality diverse titles at the best possible prices.
 Because of the quality of submissions, we doubled our investment, purchasing a total of $1 million in inventory from Lee & Low Books and HarperCollins Publishers. It was a big investment and from an unconventional source – a nonprofit social enterprise — but we knew the demand was there. And, while First Book has long benefitted from terrific partnerships with publishers, by putting $1 million on the table, we were able to really get the attention of publishers and underscore that this market exists.
Because of the quality of submissions, we doubled our investment, purchasing a total of $1 million in inventory from Lee & Low Books and HarperCollins Publishers. It was a big investment and from an unconventional source – a nonprofit social enterprise — but we knew the demand was there. And, while First Book has long benefitted from terrific partnerships with publishers, by putting $1 million on the table, we were able to really get the attention of publishers and underscore that this market exists.
It is important to note – and those of you at Lee & Low have been saying this for decades — that it’s not just kids from low-income families who need diverse books. We are all living in a more diverse world and books can help develop empathy and expand understanding. By working with publishers to develop the market for more inclusive content for our educators, First Book is also reducing the costs for publishers to make that same content available at retail. For example, First Book served as a catalyst for the development of bilingual versions of The Very Hungry Caterpillar and Goodnight Moon – and now both are also available at retail.
This spring First Book worked with Target, a longtime corporate partner, to offer three of our new Stories for All project titles for sale at retail. It is actions like those by corporations that are needed to demonstrate the broader market – and that these are, indeed, Stories for All.
We have continued to roll out strategies expanding our purchasing power to drive development of the content requested by educators serving kids in need, reduce publishers’ risk and demonstrate that there is a viable market that publishers can count on. Stay tuned!
On the publishing side, we’ve definitely seen awareness increase over the last year regarding the need for more diversity in books. Have you seen the demand increase in terms of what educators are looking for as well? How in touch (or out of touch) do you think publishing is with the current needs of educators, especially educators in low-income communities?

Yes, we’ve definitely seen an increase in the demand for diverse books from educators. In fact, this spring alone we brought 60,000 new books to our Stories for All project, and those books have been among our top 10 best-selling books every month since we launched the project!
As a society we are becoming increasingly more diverse, and our classrooms and community programs reflect that. But I also think that the demand has increased because educators know that First Book is listening – and responding – to what they need. Stories for All is bringing much-needed content that celebrates different ethnicities, cultures and languages. But it is also a catalyst for books with characters and stories that celebrate different family structures, sexual identities, individual abilities, and experiences. We are working hand-in-hand with educators and publishers to provide a full range of content, in as many forms as possible, so that children can see themselves in books and can learn about others as well.
Publishers are definitely in touch with the fact that educators working with kids from low-income families have unique needs that have not been served. They are eager to provide the content that is needed – and to a person, want to hear the input provided by First Book’s network. Publishers are an extraordinary and talented group of people. We are inspired by their commitment to our cause.
The Stories for All project, which purchases large quantities of diverse books directly from publishers, is only one of several First Book initiatives addressing the issue of diversity in books. Could you share some of the others?
The Stories for All project is, in many ways, emblematic of First Book’s work and mission as a whole. Our goal is to ensure that kids who are growing up in low-income families benefit from the same high quality books, resources and educational opportunities as their more affluent peers.
We’re undertaking a range of initiatives to support diverse books – and to make sure those books reach kids who need them. With funding from Disney, for example, First Book undertook a concerted Latino community outreach effort. This effort included providing best-in-class books and resources to programs and schools serving children from low-income families in Latino communities. As part of this effort, First Book:
- introduced more than 35,000 new Latino-serving groups to the First Book network.
- distributed more than 270,000 culturally relevant books (retail value: $2.16 million) to schools and programs serving Latino children in need.

- expanded partnerships with 50 organizations serving Latino children across the U.S.
First Book has curated collections of books on topics ranging from the experience of being an immigrant, to children with special needs and abilities, books on Muslim Americans and populations with other religions, books on Native American interests, books on LGBTQ and books on experiencing homeless and violence.
Did you receive any pushback from board members, donors, or anyone else when First Book announced any of these initiatives? If so, how did you address it?
There has been no pushback; in fact, just the opposite! We’ve had enormous support for Stories for All and our broader efforts to increase the diversity in children’s books – once people hear about it. Our biggest challenge is getting the word out. I can imagine that all of you at Lee & Low sometimes feel the same way. You’ve been pioneers in publishing diverse books and supporting diverse authors and illustrators, on the forefront of promoting stories that need to be heard.
Now that more people recognize the need for more diverse books, there seems to be a lot of hand-wringing over the issue. But hand-wringing only gets you sore hands. The only solution that will work is a market based one: people need to buy diverse books.
Looking forward, what is your vision for the role nonprofits can play in the movement for more diversity in books? Anything on the horizon that you’re excited about?
Nonprofits have a critical role in supporting diversity in books. One example: We’ve all benefitted from the work of We Need Diverse Books to raise awareness of the need for diverse books and to provide another voice for the amazing authors and illustrators who are behind those stories.
 As nonprofits, we need to put our money where our mission is – buying and featuring diverse books. First Book works with any and all nonprofits, programs serving 70% or more kids in need as well as Title I classrooms. By joining the First Book Network, nonprofits can have a real voice in developing the pipeline of resources they need.
As nonprofits, we need to put our money where our mission is – buying and featuring diverse books. First Book works with any and all nonprofits, programs serving 70% or more kids in need as well as Title I classrooms. By joining the First Book Network, nonprofits can have a real voice in developing the pipeline of resources they need.
I’m excited about several major areas of development for First Book. I am thrilled by the partnerships that we are developing. Working side-by-side with other nonprofits, like Feeding America and Share Our Strength on initiatives that combine meal support with books – during the school year and especially during the summer. Also, we’re partnering with the nonprofit Jack and Jill of America, Inc. on a virtual book drive to bring books to the Children’s Defense Fund’s Freedom Schools in honor of Marian Wright Edelman, one of my personal heroes. For our outreach effort around our Latino Culture and Heritage book collection, we’ve worked with a wide range of nonprofits – from the Cesar Chavez Foundation to the League of United Latin American Citizens, the Texas Hunger Initiative and Too Small to Fail.
I’m a strong believer that we will all achieve more impact for kids when we work collaboratively: across sectors, with dedicated nonprofits and with committed corporate partners. We are only beginning to scratch the surface of what we can do – and literally, the ideas and potential for collaborating keep me and my team continually inspired!
 Kyle Zimmer is President, CEO and Co-founder of First Book, a nonprofit social enterprise that has provided more than 130 million free and low-cost books and educational resources to schools and programs serving children in need across the U.S. and Canada. Kyle is a passionate advocate for social entrepreneurship, and the importance of literacy to further economic competitiveness and global understanding. Her awards include the National Book Foundation’s 2014 Literarian Award for Outstanding Service to the American Literary Community.
Kyle Zimmer is President, CEO and Co-founder of First Book, a nonprofit social enterprise that has provided more than 130 million free and low-cost books and educational resources to schools and programs serving children in need across the U.S. and Canada. Kyle is a passionate advocate for social entrepreneurship, and the importance of literacy to further economic competitiveness and global understanding. Her awards include the National Book Foundation’s 2014 Literarian Award for Outstanding Service to the American Literary Community.







 Frané Lessac has illustrated more than thirty-five books for young readers, several of which she has also written. Her husband, Mark Greenwood, is the author of numerous children’s books published in both the United States and his native Australia. They live in Fremantle, West Australia.
Frané Lessac has illustrated more than thirty-five books for young readers, several of which she has also written. Her husband, Mark Greenwood, is the author of numerous children’s books published in both the United States and his native Australia. They live in Fremantle, West Australia.